How moles work and why we'd care
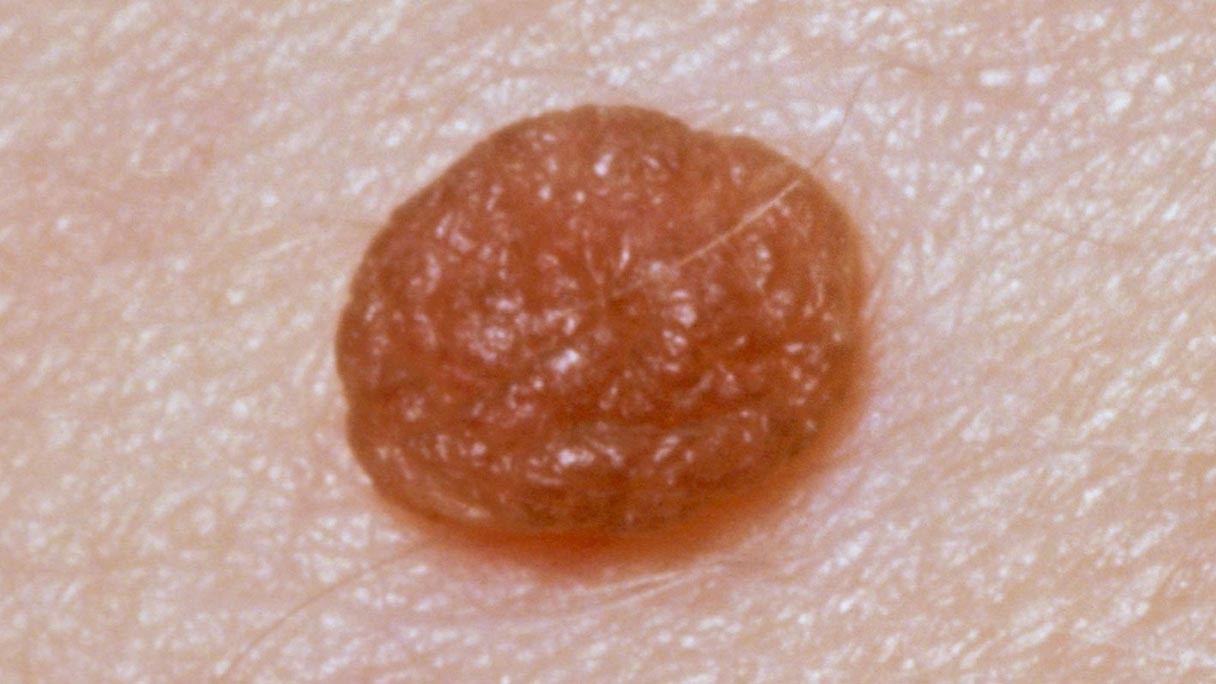
Moles are small, colored spots on the skin. Most people have them and they're usually nothing to worry about unless they change size, shape or color.
It's normal for:
When a mole could be serious? Watch out the following.
Some moles can be a sign of melanoma, a type of skin cancer.
Signs of melanoma , a form of skin cancer, include:
These changes can happen over weeks or months, and if that happens you should book a visit with your medical doctor.
UV light from the sun can increase the chance of a mole becoming cancerous. If you have lots of moles, you need to be extra careful in the sun.
It's important to check your moles regularly for any changes.
There are some things you can do to protect your moles from sun damage, especially during hot weather.
stay in the shade between 11am and 3pm, when sunlight is strongest
cover skin with clothes – wear a hat and sunglasses if you have moles on your face
regularly apply a high-factor sunscreen
do not use sunlamps or sunbeds – they use UV light
Melanoma
It's a serious form of skin cancer [2] and it begins in cells known as melanocytes.
While it is less common than basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), melanoma is more dangerous because of its ability to spread to other organs more rapidly if it is not treated at an early stage.
Melanocytes are skin cells found in the upper layer of skin. They produce a pigment known as melanin, which gives skin its color. There are two types of melanin: eumelanin and pheomelanin. When skin is exposed to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds, it causes skin damage that triggers the melanocytes to produce more melanin, but only the eumelanin pigment attempts to protect the skin by causing the skin to darken or tan. Melanoma occurs when DNA damage from burning or tanning due to UV radiation triggers changes (mutations) in the melanocytes, resulting in uncontrolled cellular growth.
Naturally darker-skinned people have more eumelanin and naturally fair-skinned people have more pheomelanin. While eumelanin has the ability to protect the skin from sun damage, pheomelanin does not. That's why people with darker skin are at lower risk for developing melanoma than fair-skinned people who, due to lack of eumelanin, are more susceptible to sun damage, burning and skin cancer.
Melanoma is usually curable when detected and treated early. Once melanoma has spread deeper into the skin or other parts of the body, it becomes more difficult to treat and can be deadly.
The estimated five-year survival rate for U.S. patients whose melanoma is detected early is about 99 percent.
An estimated 7,180 people (4,600 men and 2,580 women) will die of melanoma in the U.S. in 2021. [3]
Signs to look out for include a mole that's:
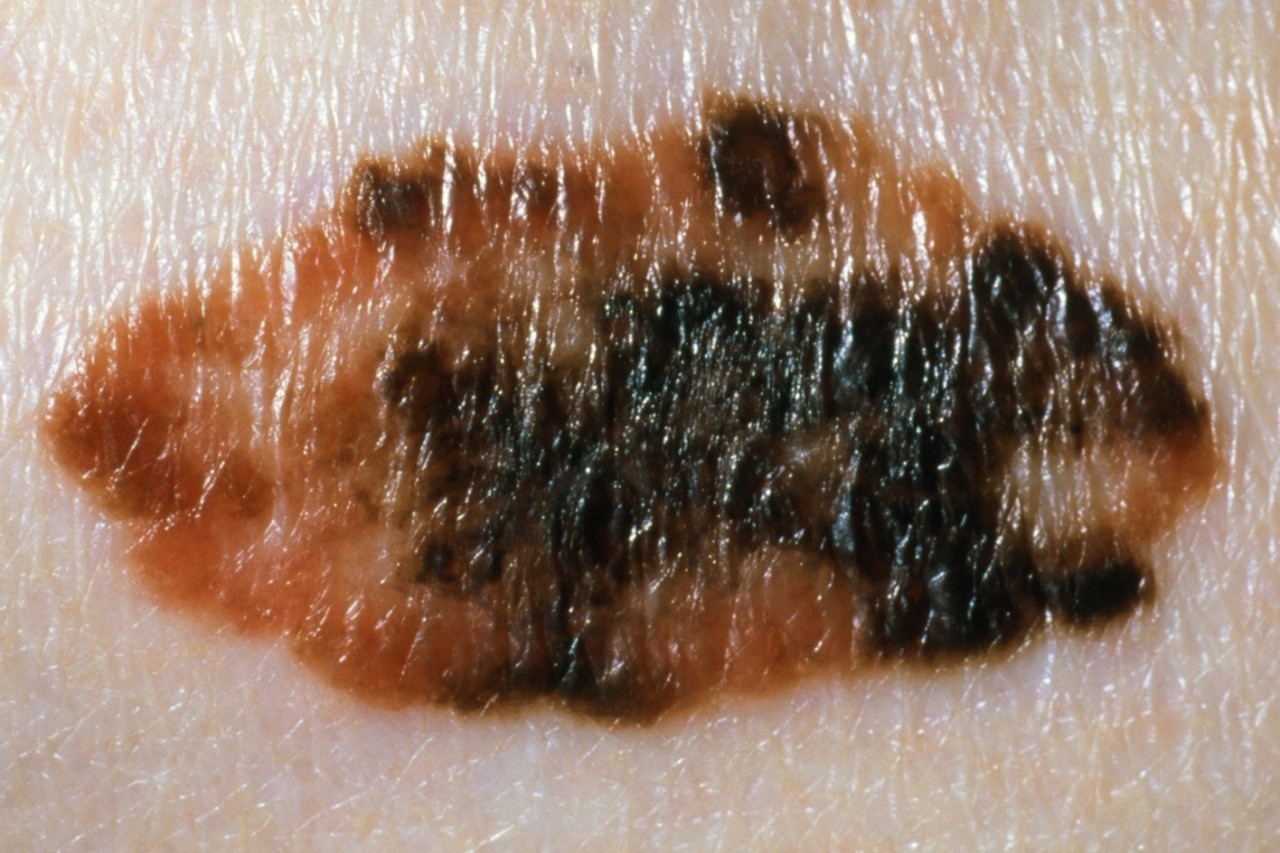
The ABCDE checklist should help you tell the difference between a normal mole and a melanoma:
Asymmetrical – melanomas usually have 2 very different halves and are an irregular shape
Border – melanomas usually have a notched or ragged border
Colors – melanomas will usually be a mix of 2 or more colors
Diameter – most melanomas are usually larger than 6mm in diameter
Enlargement or elevation – a mole that changes size over time is more likely to be a melanoma
Melanoma can appear anywhere on your body, but they most commonly appear on the back in men and on the legs in women.
It can also develop underneath a nail, on the sole of the foot, in the mouth or in the genital area, but these types of melanoma are rare.
Melanomas present in many different shapes, sizes and colors. That's why it's tricky to provide a comprehensive set of warning signs.
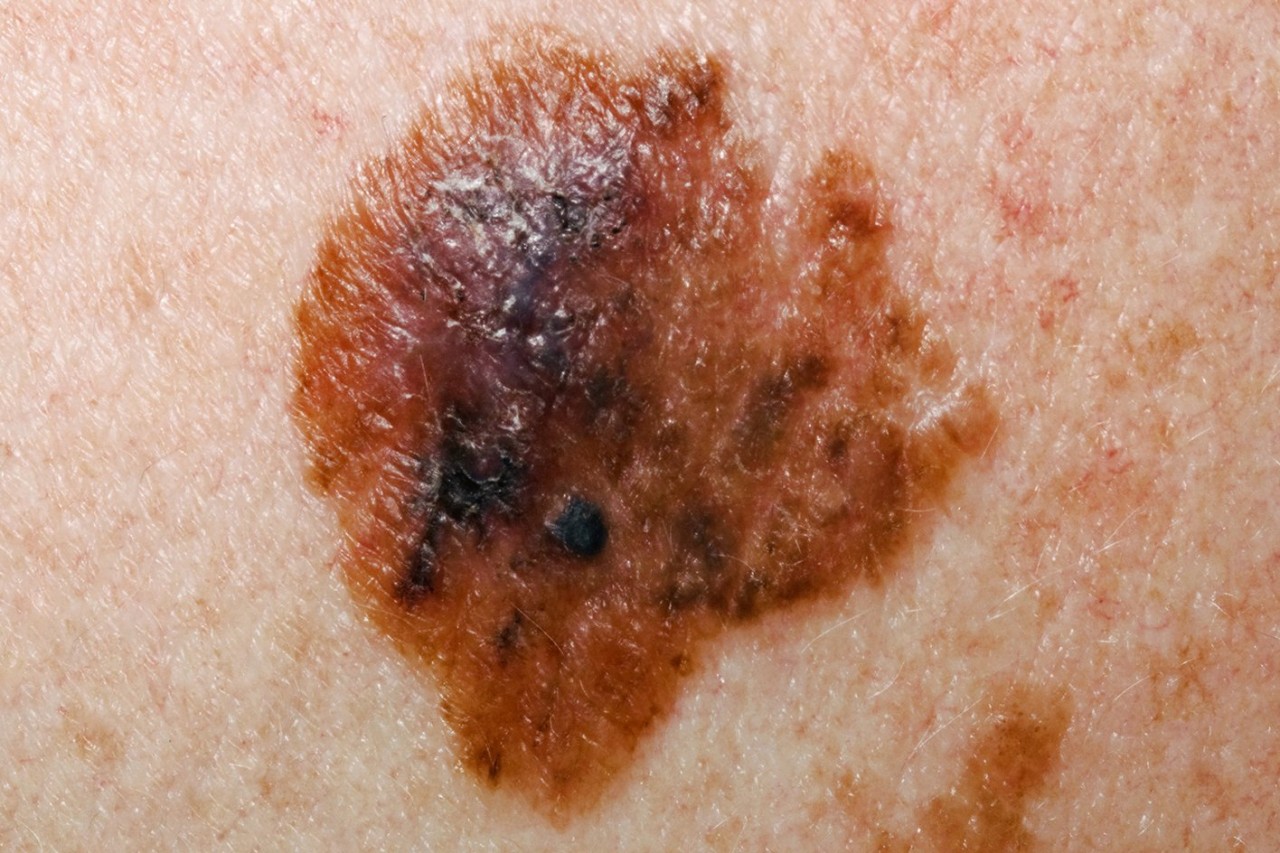
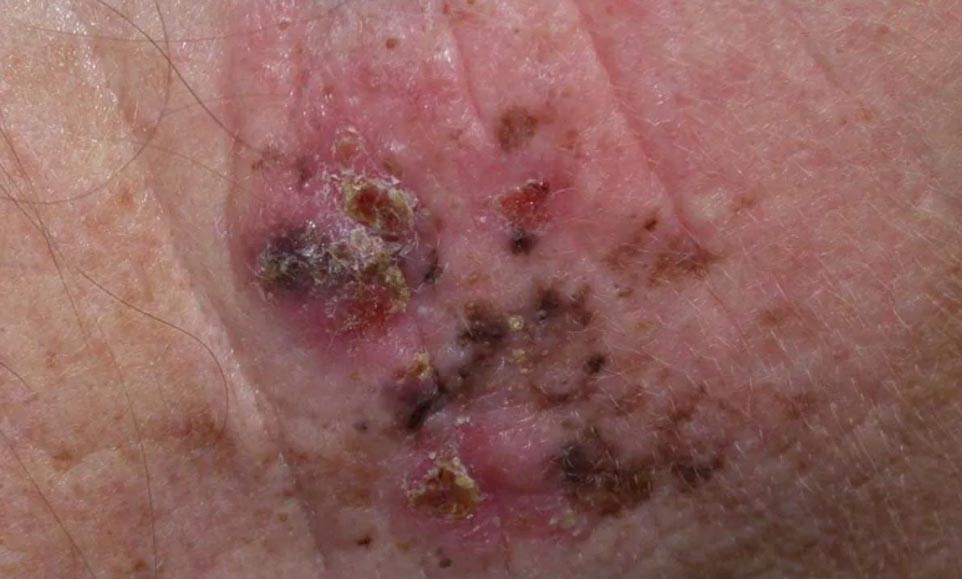
Superficial spreading melanoma is the most common form of melanoma.
It may appear as a flat or slightly raised and discolored, asymmetrical patch with uneven borders. Colors include shades of tan, brown, black, red/pink, blue or white. It can also lack pigment and appear as a pink or skin-tone lesion
Lentigo maligna often develops in older people. When this cancer becomes invasive or spreads beyond the original site, the disease is known as lentigo maligna melanoma.
It may look like a flat or slightly raised, blotchy patch with uneven borders. Color is usually blue-black, but can vary from tan to brown or dark brown.
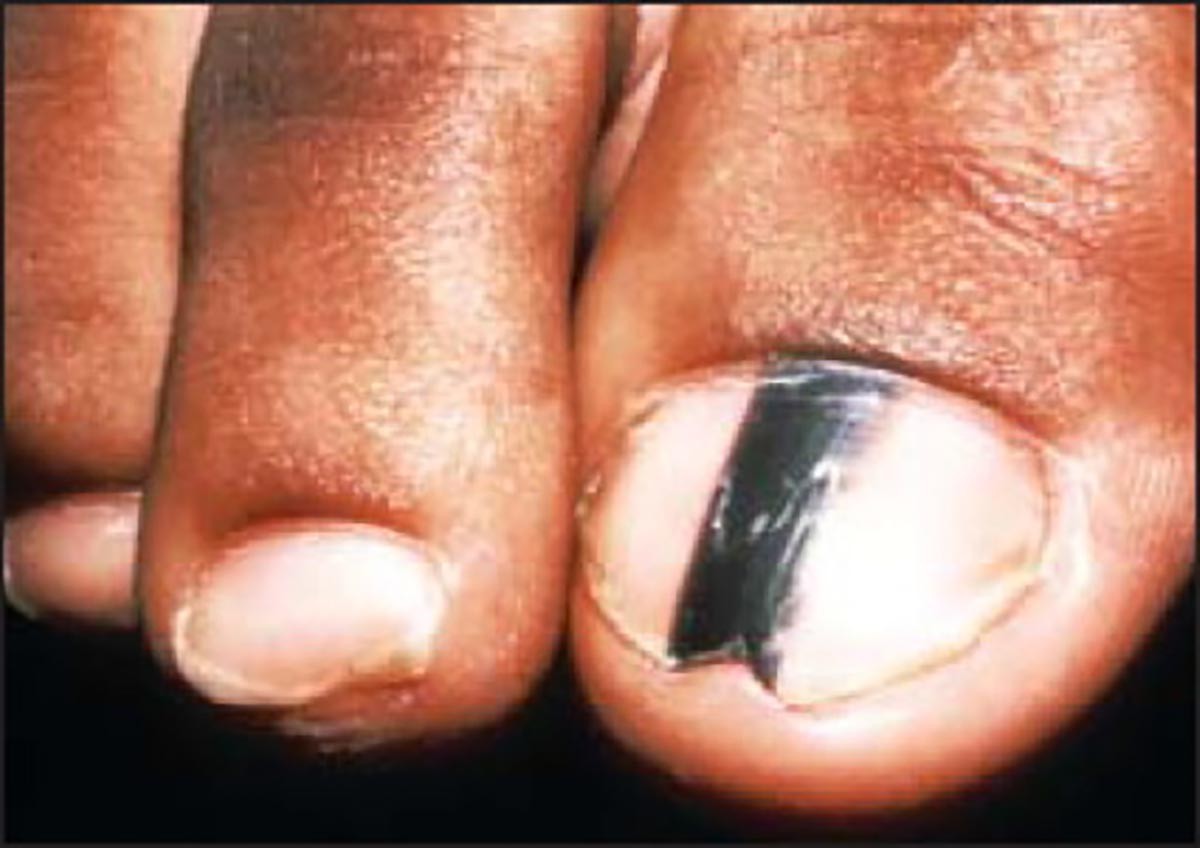
Acral lentiginous melanoma is the most common form of melanoma found in people of color, including individuals of African ancestry.
It may appear as a black or brown area.
Musician Bob Marley was diagnosed with acral lentiginous melanoma, which ultimately claimed his life at age 36.
ALM does not appear to be related to sun exposure. In some people, it may be due to a genetic risk factor.
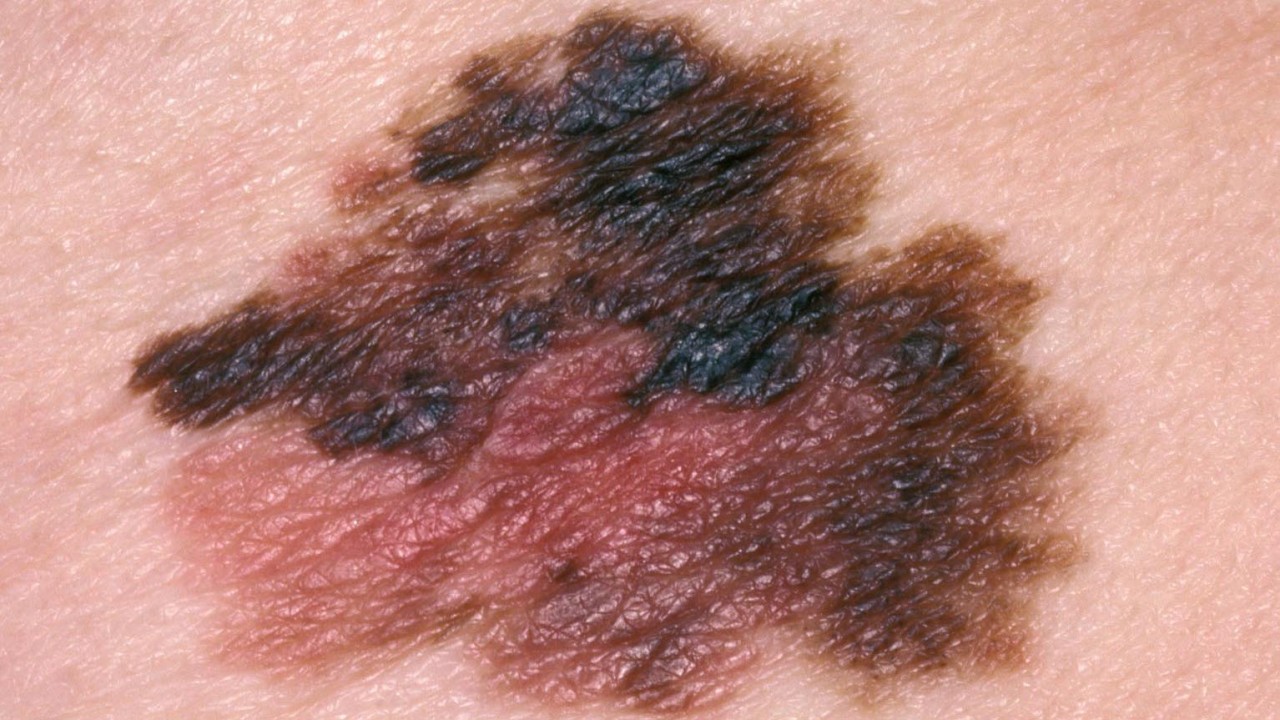
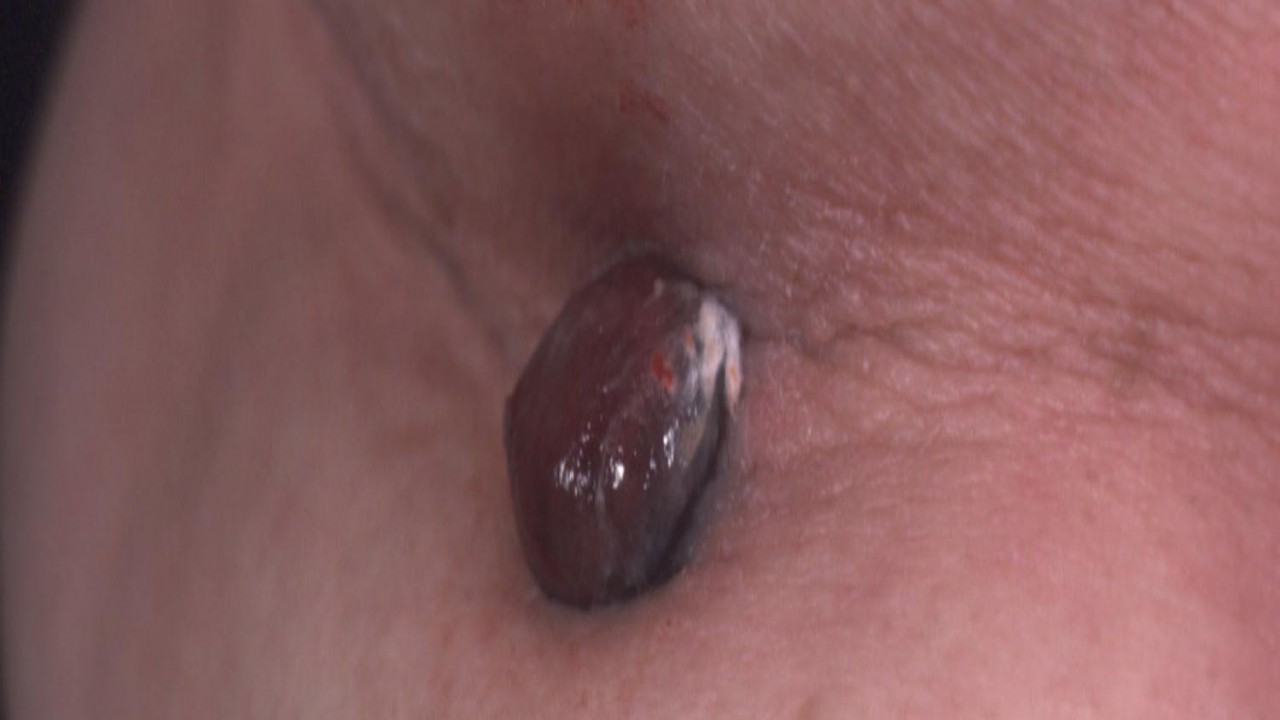
Nodular melanoma is the most aggressive type of melanoma. It accounts for 10 to 15 percent of all cases.
Nodular melanoma is often recognized as a bump on the skin, usually blue-black in color, but not uncommonly can also appear as a pink to red bump.
Nodular melanomas are a faster-developing type of melanoma that can quickly grow downwards into the deeper layers of skin if not removed.
[1] https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/moles/
[2] https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/melanoma-skin-cancer/symptoms/
[3] https://www.skincancer.org/skin-cancer-information/melanoma/
It's normal for:
- babies to be born with moles
- new moles to appear – especially in children and teenagers
- moles to fade or disappear as you get older
- moles to get slightly darker during pregnancy
- moles to have hair growing from them
When a mole could be serious? Watch out the following.
Some moles can be a sign of melanoma, a type of skin cancer.
Signs of melanoma , a form of skin cancer, include:
- A mole that's changed color or has more than 2 colors
- A mole with uneven borders
- A mole that's bleeding, itching, crusting or raised
These changes can happen over weeks or months, and if that happens you should book a visit with your medical doctor.
UV light from the sun can increase the chance of a mole becoming cancerous. If you have lots of moles, you need to be extra careful in the sun.
It's important to check your moles regularly for any changes.
There are some things you can do to protect your moles from sun damage, especially during hot weather.
stay in the shade between 11am and 3pm, when sunlight is strongest
cover skin with clothes – wear a hat and sunglasses if you have moles on your face
regularly apply a high-factor sunscreen
do not use sunlamps or sunbeds – they use UV light
Melanoma
It's a serious form of skin cancer [2] and it begins in cells known as melanocytes.
While it is less common than basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), melanoma is more dangerous because of its ability to spread to other organs more rapidly if it is not treated at an early stage.
Melanocytes are skin cells found in the upper layer of skin. They produce a pigment known as melanin, which gives skin its color. There are two types of melanin: eumelanin and pheomelanin. When skin is exposed to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds, it causes skin damage that triggers the melanocytes to produce more melanin, but only the eumelanin pigment attempts to protect the skin by causing the skin to darken or tan. Melanoma occurs when DNA damage from burning or tanning due to UV radiation triggers changes (mutations) in the melanocytes, resulting in uncontrolled cellular growth.
Naturally darker-skinned people have more eumelanin and naturally fair-skinned people have more pheomelanin. While eumelanin has the ability to protect the skin from sun damage, pheomelanin does not. That's why people with darker skin are at lower risk for developing melanoma than fair-skinned people who, due to lack of eumelanin, are more susceptible to sun damage, burning and skin cancer.
Melanoma is usually curable when detected and treated early. Once melanoma has spread deeper into the skin or other parts of the body, it becomes more difficult to treat and can be deadly.
The estimated five-year survival rate for U.S. patients whose melanoma is detected early is about 99 percent.
An estimated 7,180 people (4,600 men and 2,580 women) will die of melanoma in the U.S. in 2021. [3]
Signs to look out for include a mole that's:
- getting bigger
- changing shape
- changing colour
- bleeding or becoming crusty
- itchy or sore
The ABCDE checklist should help you tell the difference between a normal mole and a melanoma:
Asymmetrical – melanomas usually have 2 very different halves and are an irregular shape
Border – melanomas usually have a notched or ragged border
Colors – melanomas will usually be a mix of 2 or more colors
Diameter – most melanomas are usually larger than 6mm in diameter
Enlargement or elevation – a mole that changes size over time is more likely to be a melanoma
Melanoma can appear anywhere on your body, but they most commonly appear on the back in men and on the legs in women.
It can also develop underneath a nail, on the sole of the foot, in the mouth or in the genital area, but these types of melanoma are rare.
Melanomas present in many different shapes, sizes and colors. That's why it's tricky to provide a comprehensive set of warning signs.
Superficial spreading melanoma is the most common form of melanoma.
It may appear as a flat or slightly raised and discolored, asymmetrical patch with uneven borders. Colors include shades of tan, brown, black, red/pink, blue or white. It can also lack pigment and appear as a pink or skin-tone lesion
Lentigo maligna often develops in older people. When this cancer becomes invasive or spreads beyond the original site, the disease is known as lentigo maligna melanoma.
It may look like a flat or slightly raised, blotchy patch with uneven borders. Color is usually blue-black, but can vary from tan to brown or dark brown.
Acral lentiginous melanoma is the most common form of melanoma found in people of color, including individuals of African ancestry.
It may appear as a black or brown area.
Musician Bob Marley was diagnosed with acral lentiginous melanoma, which ultimately claimed his life at age 36.
ALM does not appear to be related to sun exposure. In some people, it may be due to a genetic risk factor.
Nodular melanoma is the most aggressive type of melanoma. It accounts for 10 to 15 percent of all cases.
Nodular melanoma is often recognized as a bump on the skin, usually blue-black in color, but not uncommonly can also appear as a pink to red bump.
Nodular melanomas are a faster-developing type of melanoma that can quickly grow downwards into the deeper layers of skin if not removed.
[1] https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/moles/
[2] https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/melanoma-skin-cancer/symptoms/
[3] https://www.skincancer.org/skin-cancer-information/melanoma/